Manage Pipeline#
This section describes how to create custom AI pipelines for the reference implementation and the commands to manage these pipelines.
Create Pipelines#
The AI pipelines are defined by the evam_config.json file present in the helm chart.
The following is an example of the pallet defect detection pipeline, which is included in the evam_config.json file.
"pipelines": [
{
"name": "pallet_defect_detection_2",
"source": "gstreamer",
"queue_maxsize": 50,
"pipeline": "{auto_source} name=source ! decodebin ! videoconvert ! video/x-raw,format=RGB ! udfloader name=udfloader ! gvametaconvert add-empty-results=true name=metaconvert ! gvametapublish name=destination ! appsink name=appsink",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"udfloader": {
"element": {
"name": "udfloader",
"property": "config",
"format": "json"
},
"type": "object"
}
}
},
"auto_start": false,
"publish_frame": true,
"udfs": {
"udfloader": [
{
"name": "python.geti_udf.geti_udf",
"type": "python",
"device": "CPU",
"visualize": "true",
"deployment": "./resources/models/geti/pallet_defect_detection/deployment",
"metadata_converter": "null"
}
]
}
},
Customize the pipeline according to your needs. For details, see the following Edge Video Analytics Microservice documentation:
Start the Pipeline#
Follow this procedure to start the pipeline.
In the evam_config.json file in the helm chart, identify the name of the pipeline you want to start.
The name of the pipeline is defined by the name parameter.
"pipelines": [ { "name": "pipeline_name", "source": "....", "pipeline": "...." "..." } ]You use a Client URL (cURL) command to start the pipeline.
In this example, a pipeline included in this reference implementation is pallet_defect_detection_2. Start this pipeline with the following cURL command.
curl http://localhost:30107/pipelines/user_defined_pipelines/pallet_defect_detection_2 -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{ "source": { "uri": "file:///home/pipeline-server/resources/videos/warehouse.avi", "type": "uri" }, "parameters": { "udfloader": { "udfs": [ { "name": "python.geti_udf.geti_udf", "type": "python", "device": "CPU", "visualize": "true", "deployment": "./resources/models/geti/pallet_defect_detection/deployment", "metadata_converter": "null" } ] } } }'Take note of the instance ID (without quotes).
Each pipeline has its instance ID. You will need the instance ID to stop the pipeline later.
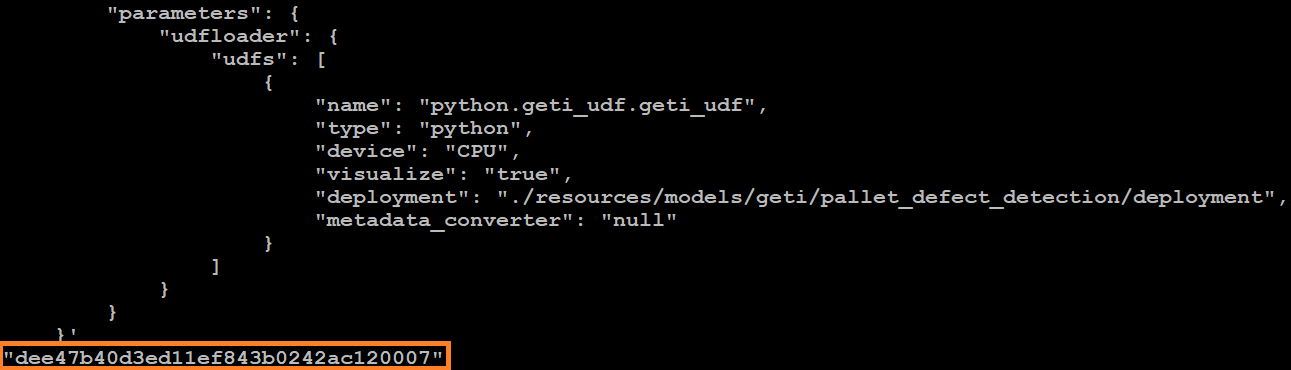
Figure 1: Example of a pipeline instance ID
Get Statistics of the Running Pipelines#
Request the pipeline statistics with this cURL command.
Replace HOST_IP with the IP address of your system.
curl --location -X GET http://<HOST_IP>:30107/pipelines/status
Stop the Pipeline#
Stop the pipeline with the following cURL command.
Replace HOST_IP with the IP address of your system and instance_id with the instance ID (without quotes) of the running pipeline.
curl --location -X DELETE http://<HOST_IP>:30107/pipelines/{instance_id}
Note
The instance ID is shown in the Terminal when the pipeline was started or when pipeline statistics was requested.
